Friday, September 10, 2021
Today’s BLOG entry is about a simple hack that can make your life easier when working with serial USB devices under Linux (Ubuntu/Debian). Every time a device is attached, an automatically generated device name is assigned to it by the OS (e.g. /dev/ttyUSB1). When you work a lot with embedded devices, using their serial USB devices for developing and testing, it could be a real pain to always change their names in a terminal program or some config files. Especially when using multiple devices concurrent, connecting and disconnecting them in different order, creates a device name lottery and very quickly you no longer know which device is connected to which device name.
[Read more…]
The prototype of my simple FPGA based SoC with multiple Ethernet interfaces worked so well that I decided to create a PCB for it and increase the number of network interfaces from two to four. It also includes a special PMOD connector for a SD-Card to boot a firmware or Linux from. Also two of the Arty’s four existing PMODs are also still available for extensions. PMOD-C and PMOD-D are no longer available as their pins are used for some of the Ethernet PHY modules.
Due to I/O limitations the Seven Segment Display was removed from the original design.
[Read more…]
Recently, for a project, I needed to work with ns2 (1), (2). Adding own protocols to ns2 requires to compile it from the sources instead of just installing it via apt-get.
It has a lot of dependencies (e.g. tcl/tk) which where already installed on my system. According to here there is a all-in-one package of ns2 including ALL its dependencies. As my machine is always near to 100% full and I already have installed its dependencies for other projects I just downloaded ns2 source without dependencies. Downloading the sources and the well known stanza ‘configure / make / make install’ should be enough - I though.
But alas - configure didn’t find required dependencies. OK - so fix some paths to keep configure happy. But now lots of compile time errors occurred. I’m running on Ubuntu Linux 16.04 LTS 64bit and a lot of include files and libraries are not there where ns2’s configure script expects it to find. It also seems that ns2’s dependencies installed via apt-get have been compiled with different compile time options as ns2 expects. Google did not help much and so I decided to fix things so that I can successfully compile ns2 an start hacking new protocols.
This post shows the steps and also provides the patches.
Step 1: Install prerequisites (from package repository)
sudo apt-get install \
tcl8.6 libtcl8.6 tcl8.6-dev \
tk8.6 tk8.6-dev \
libotcl1 libotcl1-dev \
tclcl libtclcl1 tclcl-dev
Step 2: Get the sources (ns2 without dependencies)
wget \
https://sourceforge.net/projects/nsnam/files/ns-2/2.35/ns-src-2.35.tar.gz/download \
-O ./ns-2.35.tgz
tar xvf ./ns-2.35.tgz
Step 3: Apply the patches
The patches can be downloaded here ns-2.35-ubuntu-16.04-64bit.patch.
patch \
-d ./ns-2.35 \
-p2 \
< ./ns-2.35-ubuntu-16.04-64bit.patch
Step 4: configure / make / make install
cd ./ns-2.35
./configure \
–with-tcl-ver=8.6 \
–with-tk-ver=8.6
make
Now you should have a ns binary in ns2 source folder. To ensure that ns2 compiled correctly, run validate to perform tests (warning: this takes long)
Step 5: Start hacking
For more infos about ns2 and ns2 development see the following links
This steps were tested with Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 64bit and it might be that they wont work with other versions or distributions. But they may help to fix problems there too.
Wednesday, March 15, 2017
I was very pleased to give a presentation about the AMP Testbed Project at this years ESA ARTES Final Presentation Days on March, 8th 2017 at ESAs technical center ESTEC Newton conference room.
[Read more…]
Tuesday, December 13, 2016
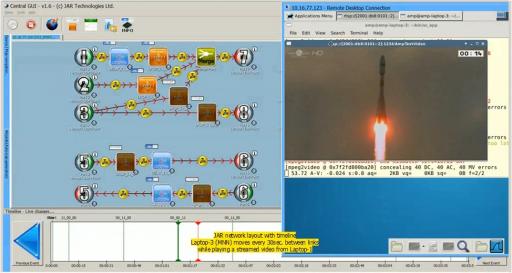
Finally after about two years of development the AMP (Advanced Mobility Protocolls) testbed developed for the European Space Agency (ESA) was delivered to its European Space Research and Technology Center (ESTEC) in Noordwijk, Netherlands.
AMP consists of a virtualization host, cisco switches, a JAR Network Emulator and some physical hosts and allows the simulation of various IPv6 mobility protocolls in a satellite context like PMIP, NEMO and MPTCP. It is completely self contained, remote controllable and can simulate even complex network layouts.
It was a pleasure to work on this project!